A Reliable Beta-Blocker for Glaucoma Management
Timolol is a beta-blocker widely used in the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Available as an eye drop, it works by reducing the production of aqueous humor in the eye, effectively lowering intraocular pressure (IOP). Its proven efficacy and relatively low cost make it a popular first-line treatment, either alone or in combination with other medications.
How Effective Is Timolol?
Timolol is highly effective in lowering IOP, achieving reductions of 20–30% on average. This makes it a strong option for managing open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It also helps to slow or prevent optic nerve damage and vision loss.
Side Effects and Precautions
While timolol is generally well-tolerated, it may cause local side effects, such as mild stinging or redness upon application. Systemic absorption, however, can lead to more serious issues, including a slowed heart rate, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or certain heart conditions should avoid timolol due to these risks.
Other rare side effects include dry eyes, blurred vision, or sensitivity to light. It is crucial for patients to inform their doctor about any existing medical conditions before starting these eye drops.
Elimination and Half-Life of Timolol
Timolol has a half-life of approximately 4–6 hours but offers long-lasting effects, allowing for twice-daily dosing. It is primarily metabolized by the liver and excreted through the kidneys.
Combination Therapy
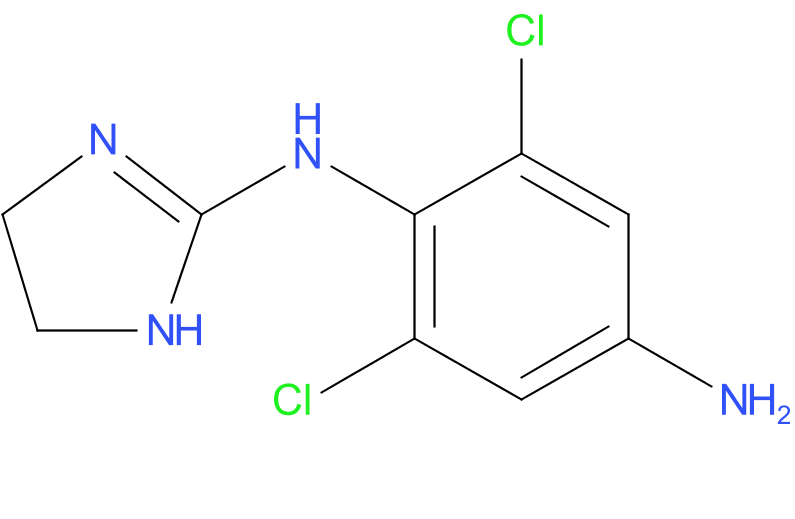
Timolol is frequently used in combination with other glaucoma medications for enhanced IOP control. Fixed-combination drops, such as timolol with dorzolamide (a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor known widely as Cosopt) or brimonidine (an alpha agonist), are common options for reducing the burden of multiple medications.
What Patients Should Know
For best results, timolol should be used as prescribed, usually in the morning and evening. Patients should press on the tear duct for 1–2 minutes after applying the drops to reduce systemic absorption. Contact lenses should be removed before application and can be reinserted after 15 minutes.
With its solid efficacy, affordability, and versatility, timolol remains essential in glaucoma management. Regular eye exams and open communication with your eye care provider will ensure optimal outcomes and vision preservation.